skiprope< T > Class Template Reference
An vector-like collection<T> which is implemented in such a way that no large blocks of memory are created. This allows inserts and deletes to be done in a time which is proportional to the size of the block being acted upon -- rather than upon the whole size of the container. To pay for _this_ performance gain, random accesses within the vector require O(ln(N)) time rather than O(1) as you usually see in a vector. Iteration is still O(1) but is much slower than iteration in a vector<T>. More...
#include <skiprope.h>


Classes | |
| struct | node_info |
| A structure describing a node in the rope. It is used in navigating the node data structure more easily than keeping track of the separate components of the description. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef skiprope_const_iterator< T > | const_iterator |
| typedef skiprope_iterator< T > | iterator |
| typedef skiprope< T > | self |
| typedef int | size_t |
Public Member Functions | |
| T const & | back () const |
| T & | back () |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| iterator | begin () |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| iterator | end () |
| void | erase (iterator first, iterator last) |
| void | erase (iterator location) |
| ptrdiff_t | find (const_iterator) const |
| const_iterator | find (ptrdiff_t offset) const |
| ptrdiff_t | find (iterator) |
| offset from iterator | |
| iterator | find (ptrdiff_t offset) |
| iterator to offset | |
| T const & | front () const |
| T & | front () |
| iterator | insert (iterator i, T const &r) |
| iterator | insert (iterator, T const *first, T const *last) |
| T const & | operator[] (ptrdiff_t i) const |
| T & | operator[] (ptrdiff_t i) |
| void | push_back (T const &r) |
| void | push_back (T const *first, T const *last) |
| append a bunch of T's to the end of the skiprope | |
| iterator | push_front (T const &r) |
| iterator | push_front (T const *first, T const *last) |
| When inserting at the front, it is easier than most cases because every node is already in level 0. So, for example if you have the following layout: | |
| ptrdiff_t | size () const |
| skiprope (self const &r) | |
| skiprope () | |
| ~skiprope () | |
Public Attributes | |
| int | visited_levels_ |
| debug info for test only. | |
Private Types | |
| enum | chunk_size_ { chunk_size } |
| enum | index_levels_ { max_index_levels = 32 } |
| typedef skiprope_level_desc< T > | level_desc |
| typedef skiprope_node< T > ::link_info | link_info |
| enum | max_block_size_ { max_block_size = SKIPROPE_MAX_BLOCKSIZE } |
| typedef skiprope_node< T > | node |
Private Member Functions | |
| node_info | find_node_before (ptrdiff_t location, int level) |
| get the node just before 'offset' at a given level | |
| void | insert_node (node *before, node *after) |
| int | predecessors (node *n, node_info *pred) |
| get list of pred nodes returns count of levels returned. | |
| int | prednodes (node *, node_info *pred) |
| get only node_ info into pred and return count of levels found | |
| void | predoffsets (node_info *pred, int levels) |
| compute offset_ given nodes_ | |
| void | split_node (node *n, ptrdiff_t offset) |
Private Attributes | |
| int | active_levels_ |
| hightest node level | |
| node * | last_ |
| ptr to last node in the rope gives O(1) rear access and makes end() work correctly | |
| level_desc | level_ [max_index_levels] |
| int | nodes_ |
| ptrdiff_t | size_ |
| items in the array | |
Friends | |
| struct | node_info |
| class | skiprope_const_iterator< T > |
| class | skiprope_debugger< T > |
| class | skiprope_iterator< T > |
Detailed Description
template<class T>
class cxxtls::skiprope< T >
An vector-like collection<T> which is implemented in such a way that no large blocks of memory are created. This allows inserts and deletes to be done in a time which is proportional to the size of the block being acted upon -- rather than upon the whole size of the container. To pay for _this_ performance gain, random accesses within the vector require O(ln(N)) time rather than O(1) as you usually see in a vector. Iteration is still O(1) but is much slower than iteration in a vector<T>.
The following table describes the time complexity of some normal operations:
skiprope() O(1) // create an empty skiprope ~skiprope() O(N) // destroy a skiprope operator[i] O(ln(N)) // get a reference to a specifc location find(i) O(ln(N)) // get an iterator to a specific location iterator++ O(1) // increment an iterator iterator-- O(1) // decrement an iterator iterator+int -------- // can't add numbers to iterators, use find() insert(it,T) O(ln(N)) // insert given an iterator erase(it) O(ln(N)) // erase given an iterator push_back(T) O(1) // append
This container is implemented as a sorted list of variable width blocks. The sum of the width's of the prior blocks is the start offset of this block. When inserting data into a block, no block can exceed max_block_size unless sizeof(T) is greater than max_block_size. The fact that the blocks are sorted means that you can
Each node of data (again, varying in width between nodes) is assigned 1 to max_index_levels randomly. The randomization gives the O(Ln(N)) behavior with small wasted space in the indices. Nodes are linked into at most max_index_levels of linked lists based on the level assigned to the particular node.
To get O(LN(N)) lookups for a given offset into the vector, the highest level index list is searched first. Then the list of nodes that might hold the offset in question is found.
Next, the next lower level of lists is searched to narrow the range. The narrowed range is then further narrowed by going down one more level of lists. This is repeated until the 0'th level is searched.
This simulates a binary tree but is always balanced -- ergo no rebalancing penalty is ever paid.
Definition at line 592 of file skiprope.h.
Member Typedef Documentation
| typedef skiprope_const_iterator<T> const_iterator |
Definition at line 686 of file skiprope.h.
| typedef skiprope_iterator<T> iterator |
Definition at line 684 of file skiprope.h.
typedef skiprope_level_desc<T> level_desc [private] |
Definition at line 662 of file skiprope.h.
typedef skiprope_node<T>::link_info link_info [private] |
Definition at line 660 of file skiprope.h.
typedef skiprope_node<T> node [private] |
Definition at line 659 of file skiprope.h.
Definition at line 681 of file skiprope.h.
| typedef int size_t |
Definition at line 682 of file skiprope.h.
Member Enumeration Documentation
enum chunk_size_ [private] |
Definition at line 650 of file skiprope.h.
enum index_levels_ [private] |
Definition at line 648 of file skiprope.h.
enum max_block_size_ [private] |
Definition at line 646 of file skiprope.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| skiprope | ( | ) |
Definition at line 688 of file skiprope.h.
| ~skiprope | ( | ) |
Member Function Documentation
| T const& back | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 720 of file skiprope.h.
| T& back | ( | ) |
Definition at line 719 of file skiprope.h.
| skiprope< T >::const_iterator begin | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 810 of file skiprope.h.
| skiprope< T >::const_iterator end | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 817 of file skiprope.h.


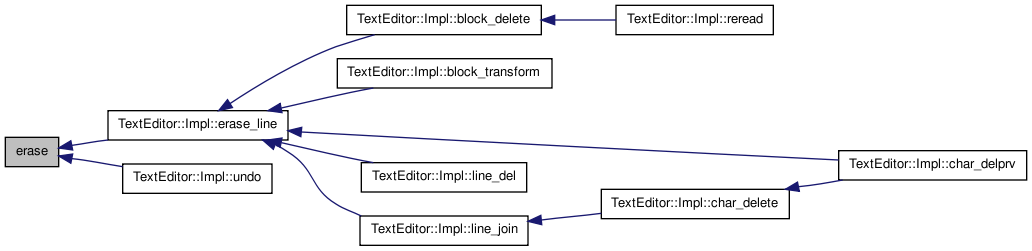
| void erase | ( | iterator | location | ) |
| ptrdiff_t find | ( | const_iterator | ) | const |
| skiprope< T >::const_iterator find | ( | ptrdiff_t | offset | ) | const |
Definition at line 953 of file skiprope.h.
| ptrdiff_t find | ( | iterator | ) |
offset from iterator
iterator to offset
Get an iterator to a specified offset within the skiprope vector.
starting at the highest active level scan across the links on each level until the sum of the widths of the links already scanned plus the width of the next link will exceed the search address. When the next link exceeds or doesn't exist, drop down a level at the same node and keep scanning until you are at level 0 or found it or out of data. The scanner moves from the top left of a graph to the bottom right where top left is the highest array index of the level_ array and offset 0 from the beginning of the simulated vector.
Each node has a width_ for each level. This width is the sum of distance of all lower level nodes between this node and the next node _this_ level. At any given level, the start address within the simulated vector of this node is the sum of width_ fields at this level prior (ie between head_ and this node).
Definition at line 845 of file skiprope.h.


get the node just before 'offset' at a given level
Definition at line 907 of file skiprope.h.

| T const& front | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 718 of file skiprope.h.
| T& front | ( | ) |
Definition at line 717 of file skiprope.h.
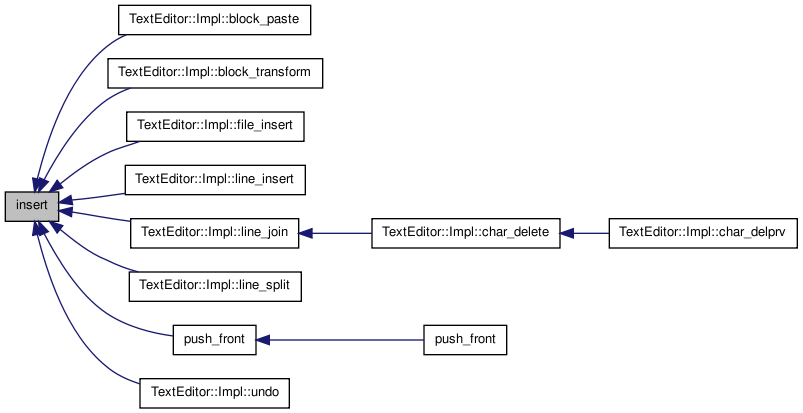
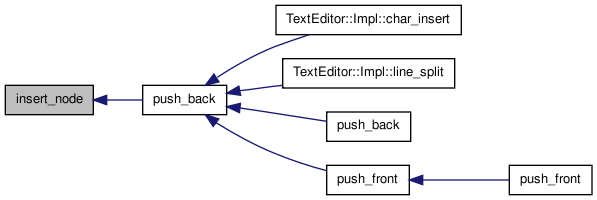
| T const& operator[] | ( | ptrdiff_t | i | ) | const |
Definition at line 706 of file skiprope.h.
| T& operator[] | ( | ptrdiff_t | i | ) |
Definition at line 699 of file skiprope.h.
get list of pred nodes returns count of levels returned.
get only node_ info into pred and return count of levels found
| void predoffsets | ( | node_info * | pred, | |
| int | levels | |||
| ) | [private] |
compute offset_ given nodes_
| void push_back | ( | T const & | r | ) |
| void push_back | ( | T const * | first, | |
| T const * | last | |||
| ) |
append a bunch of T's to the end of the skiprope
Definition at line 962 of file skiprope.h.


When inserting at the front, it is easier than most cases because every node is already in level 0. So, for example if you have the following layout:
lvl Nodes
---+---------------
3| E
2| D E
1| A C D E
0| A B C D E
Inserting at the front, if the data fits in A, means doing the following:
Adjusting the width of A (from 1 to 2, for example) adjusting the level_[].offset_ info for all nodes who have levels higher than A's: D and E.
On the other hand, if the data won't fit in the first node, we must insert a new one:
lvl Nodes
---+---------------
3| E
2| N D E
1| N A C D E
0| N A B C D E
and adjust the following:
- level_[].node_ info for levels occupied previously by A now refer to N.
- the level_[].offset_ for levels higher than N now become 0 and N's link_[].width_ member becomes the old offset_ value plus N's width.
Finally, if the data won't fit in A and also won't fit in a single node N, but has overflow components, this routine puts the part that will fit into N where it should be then calls the random insert routine to jam in the rest after N.
Definition at line 1574 of file skiprope.h.
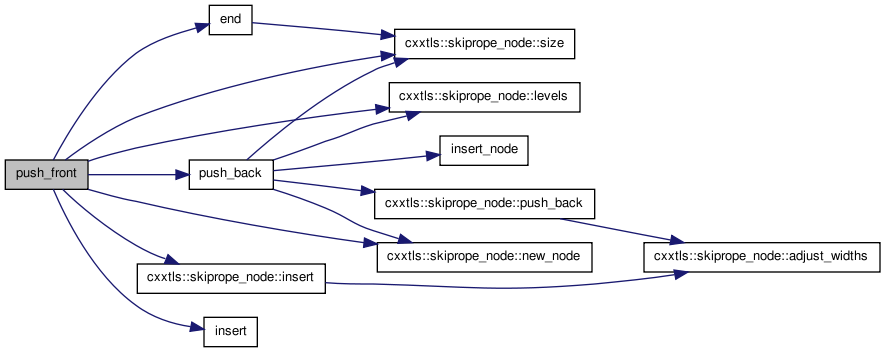

| ptrdiff_t size | ( | ) | const |
| void split_node | ( | node * | n, | |
| ptrdiff_t | offset | |||
| ) | [private] |
Friends And Related Function Documentation
friend struct node_info [friend] |
Definition at line 746 of file skiprope.h.
friend class skiprope_const_iterator< T > [friend] |
Definition at line 643 of file skiprope.h.
friend class skiprope_debugger< T > [friend] |
Definition at line 641 of file skiprope.h.
friend class skiprope_iterator< T > [friend] |
Definition at line 642 of file skiprope.h.
Member Data Documentation
int active_levels_ [private] |
hightest node level
Definition at line 671 of file skiprope.h.
ptr to last node in the rope gives O(1) rear access and makes end() work correctly
Definition at line 667 of file skiprope.h.
level_desc level_[max_index_levels] [private] |
Definition at line 664 of file skiprope.h.
int nodes_ [private] |
Definition at line 675 of file skiprope.h.
ptrdiff_t size_ [private] |
items in the array
Definition at line 673 of file skiprope.h.
| int visited_levels_ |
debug info for test only.
Definition at line 679 of file skiprope.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- include/cxxtls/skiprope.h


 1.6.3
1.6.3