FileMode Struct Reference
A representation of a file's mode (ie permissions and type). If the file is a symbolic link, the link bit will be 1, but the other bits will refer to file to which the link points. Note that this is the design of the FileMode class -- but also note that the FileMode class does not have way of populating itself. To obtain a FileMode object's value, call FileName::file_stat(&fileMode). More...
#include <file.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | bit_name { link = 010000, directory = 004000, set_uid = 002000, set_gid = 001000, user_readable = 000400, user_writeable = 000200, user_executable = 000100, group_readable = 000040, group_writeable = 000020, group_executable = 000010, world_readable = 000004, world_writeable = 000002, world_executable = 0000001 } |
names for the various permissions. Not guaranteed to be portable More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| void | construct_from_string (std::string const &s) |
| Set the mode value given a null terminated character string as defined in the constructor, FileMode(char const*). | |
| void | construct_from_string (char const *string) |
| Set the mode value given a null terminated character string as defined in the constructor, FileMode(char const*). | |
| FileMode (std::string s) | |
| Construct the mode from a 10 character std::string formatted as in the constructor, FileMode(char const*). | |
| FileMode (char const *s) | |
| Construct a FileMode from the os' permissions object from an an integer. | |
| FileMode (int m) | |
| FileMode() default constructor. | |
| FileMode () | |
| bool | is_dir () const |
| is_dir() | |
| bool | is_link () const |
| An inline method indicating that the file is really a symbolic link that points to some file somewhere that has the OTHER attributes defined by the mode member variable. | |
| operator std::string () const | |
| convert the permissions to a string | |
| int | os_mode () const |
| return an integer that _is_ the os specific representation of this generic FileMode object. In the case of symbolic link files, the os_mode() returns the link target's stat::st_mode value. | |
| void | packPermissions (std::string const &userMode, std::string const &groupMode, std::string const &worldMode) |
| Modify the permissions part of this file mode with data supplied in std::strings. Each mode sub-set (group, user, world) will look like this: rwx. | |
| bool | permStringValid (std::string const &string) |
| Return true if the string contains only valid permissions -- permissions must look like this: rwx. | |
| void | unpackPermissions (std::string &userMode, std::string &groupMode, std::string &worldMode) |
| Split this FileMode object into std::strings representing the permissions. Each permission std::string will look like this: rwx. | |
Public Attributes | |
| int | mode |
| mode The integer representation of the mode, not necessarily the os representation! | |
Friends | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &o, FileMode const &r) |
| operator<<(stream, FileMode const&) prints the permissions to an output stream | |
Detailed Description
A representation of a file's mode (ie permissions and type). If the file is a symbolic link, the link bit will be 1, but the other bits will refer to file to which the link points. Note that this is the design of the FileMode class -- but also note that the FileMode class does not have way of populating itself. To obtain a FileMode object's value, call FileName::file_stat(&fileMode).
To find the mode of the symbolic link file itself (ie without any reference to its target) use the FileName::readlink(&mode) function call. Here's an example use:
FileStatus fs;
FileName someFile("someFile");
if(someFile.file_stat(&fs)) { // an error has occurred }
if(fs.mode & FileMode::user_readable) { // the file's owner (ie user) can read it }
Note that there is a long list of permission bits to test against.
Definition at line 187 of file file.h.
Member Enumeration Documentation
| enum bit_name |
names for the various permissions. Not guaranteed to be portable
- Enumerator:
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| FileMode | ( | int | m | ) |
FileMode() default constructor.
| FileMode | ( | char const * | s | ) |
Construct a FileMode from the os' permissions object from an an integer.
The permissions integer is assumed to be struct stat's member st_mode Construct the mode from a 10 character string formatted like this:
drwxrwxrwx -rw-rw-rw-
etc.
Definition at line 242 of file file.h.

| FileMode | ( | std::string | s | ) |
Construct the mode from a 10 character std::string formatted as in the constructor, FileMode(char const*).
Definition at line 254 of file file.h.

Member Function Documentation
| void construct_from_string | ( | std::string const & | s | ) |
Set the mode value given a null terminated character string as defined in the constructor, FileMode(char const*).
Definition at line 268 of file file.h.

| void construct_from_string | ( | char const * | string | ) |
Set the mode value given a null terminated character string as defined in the constructor, FileMode(char const*).
Definition at line 329 of file file.cxx.


| bool is_dir | ( | ) | const |
An inline method indicating that the file is a directory. 'is_dir' is provided only as an example to see show how the bits in the permissions work. For the other bits, you should see is_dir's implementation and manually access the individual bits.
Definition at line 299 of file file.h.
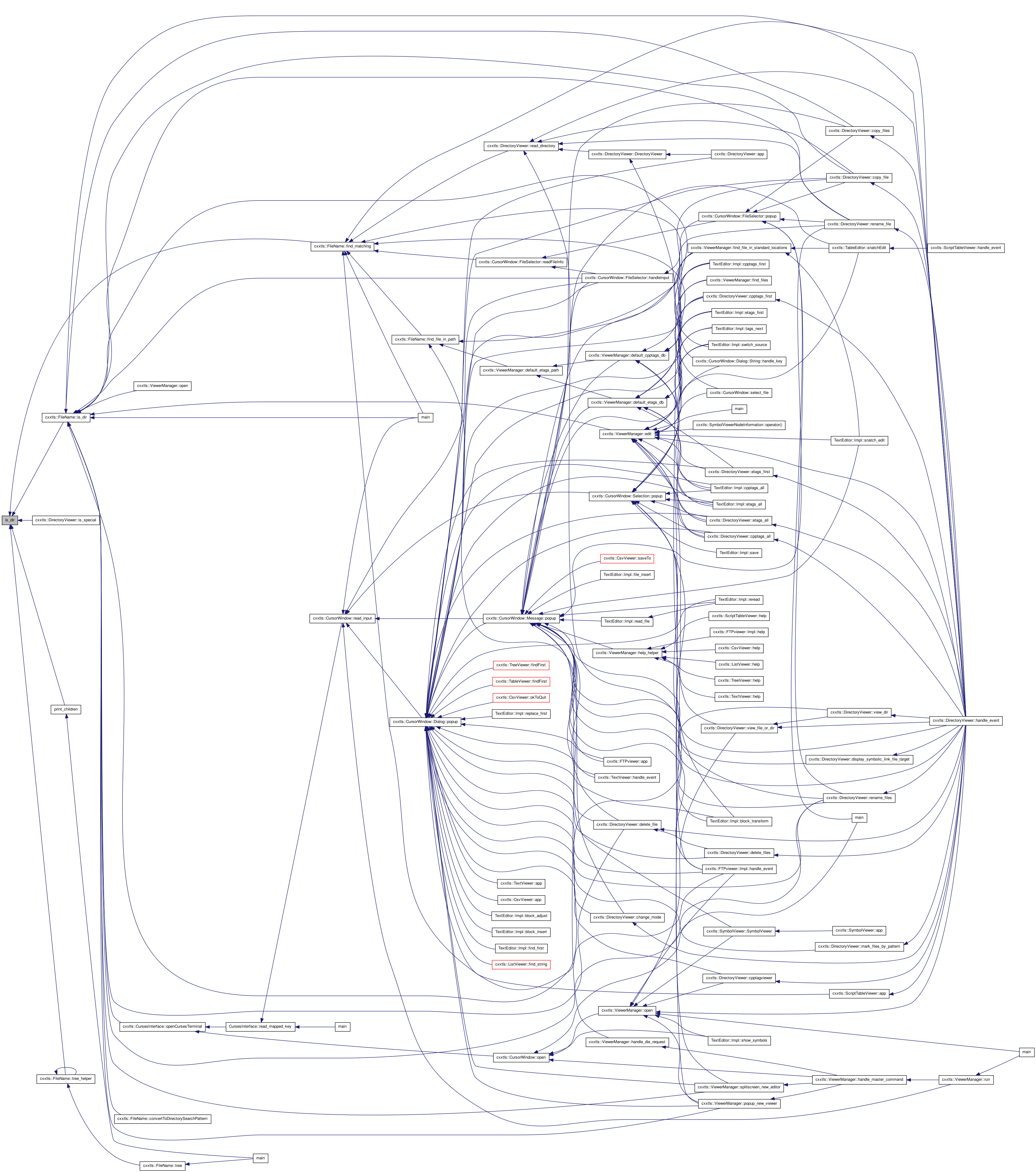
| bool is_link | ( | ) | const |
An inline method indicating that the file is really a symbolic link that points to some file somewhere that has the OTHER attributes defined by the mode member variable.
The function, FileName::file_stat(), reads through symbolc links to get the real attributes of the file being pointed to by the link and it is these attributes that are described by FileMode::mode. However, the link bit is also set.
You can use FileName::readlink() to get the file name referred to by the link. It is that file whose attributes are represented by FileMode::mode.
Definition at line 308 of file file.h.

| operator std::string | ( | ) | const |
convert the permissions to a string
| int os_mode | ( | ) | const |
| void packPermissions | ( | std::string const & | userMode, | |
| std::string const & | groupMode, | |||
| std::string const & | worldMode | |||
| ) |
Modify the permissions part of this file mode with data supplied in std::strings. Each mode sub-set (group, user, world) will look like this: rwx.
Bits in the mode that are not part of the file permissions are not modified by this method
Definition at line 2590 of file file.cxx.


| bool permStringValid | ( | std::string const & | string | ) |
Return true if the string contains only valid permissions -- permissions must look like this: rwx.
Letters can be left out, upper case is ok, but letters may not be duplicated and no other letters, spaces, or -'s can appear
Definition at line 2616 of file file.cxx.

| void unpackPermissions | ( | std::string & | userMode, | |
| std::string & | groupMode, | |||
| std::string & | worldMode | |||
| ) |
Friends And Related Function Documentation
| std::ostream& operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | o, | |
| FileMode const & | r | |||
| ) | [friend] |
Member Data Documentation
| int mode |
The documentation for this struct was generated from the following files:
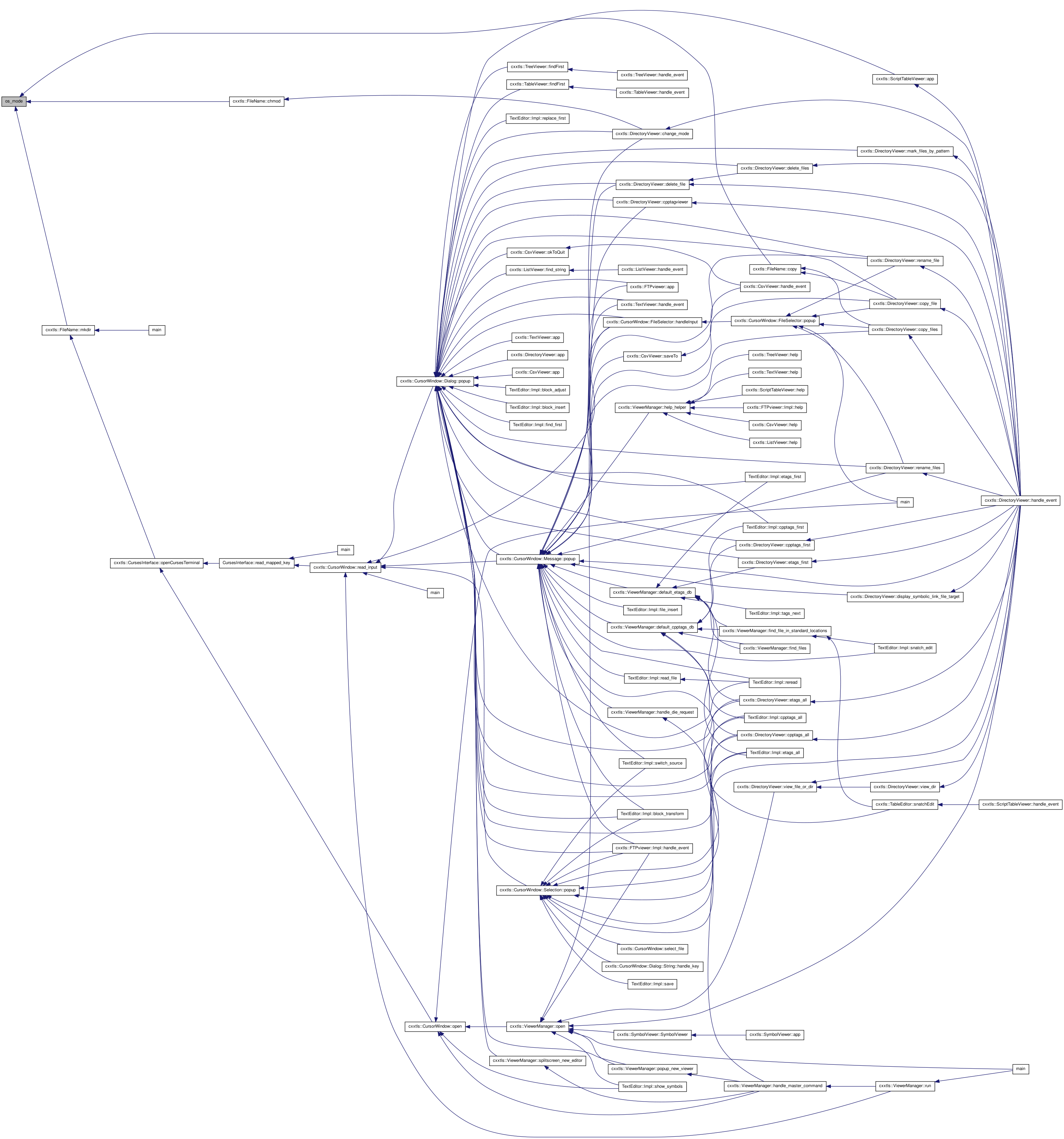

 1.6.3
1.6.3